Customer Success Manager: Roles, Requirements & Experience

The role of a Customer Success Manager (CSM) is pivotal in today’s customer-centric business landscape. Companies increasingly recognize that maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty is crucial for long-term success. A CSM is dedicated to ensuring customers achieve their desired outcomes while using a company's product or service.
This article delves into the comprehensive roles, requirements, and CSM experiences.
What is a Customer Success Manager?

A Customer Success Manager is responsible for ensuring that customers achieve their desired outcomes while using a company's products or services. They act as the bridge between the customer and the company, focusing on building long-term relationships and promoting customer loyalty.
Key Customer Success Manager Roles
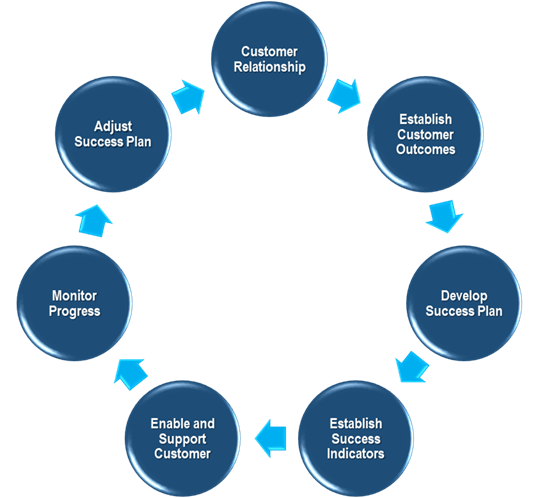
A Customer Success Manager wears many hats, including:
Understanding Customer Needs
A key role of a Customer Success Manager is to understand the unique needs and goals of each customer. By actively listening and engaging with customers, a CSM can tailor solutions that align with customer expectations. This understanding forms the foundation for all subsequent interactions and strategies.
Building Strong Customer Relationships
Establishing and nurturing strong relationships with customers is essential. A CSM must build trust and rapport, ensuring customers feel valued and understood. This relationship is critical for long-term customer retention and satisfaction.
Onboarding New Customers
Effective onboarding is vital to customer success. CSMs guide new customers through the initial stages of using a product or service, ensuring they have the necessary tools and knowledge to get started. This process sets the tone for the entire customer journey.
Providing Product Training
Offering comprehensive product training helps customers maximize the value they get from a product or service. CSMs often conduct training sessions, create instructional materials, and provide ongoing education to keep customers informed and competent.
Monitoring Customer Health
A proactive approach to monitoring customer health helps identify potential issues before they escalate. CSMs use various metrics and tools to assess customer satisfaction, engagement, and overall health, enabling timely interventions.
Facilitating Renewals and Upsells
Ensuring customers renew their subscriptions or contracts is a critical aspect of a CSM’s role. Additionally, identifying opportunities for upselling and cross-selling relevant products or services can enhance customer value and drive business growth.
Handling Customer Feedback
Customer feedback is invaluable for continuous improvement. CSMs gather and analyze feedback to understand customer pain points and areas for enhancement, ensuring the company addresses these issues effectively.
Collaborating with Sales and Marketing Teams
CSMs work closely with sales and marketing teams to ensure a seamless customer experience. This collaboration helps align efforts across departments, leading to better customer outcomes and unified business goals.
Creating Success Plans
Developing customized success plans for each customer ensures that their specific needs and goals are met. These plans outline clear steps and milestones, helping customers achieve their desired outcomes efficiently.
Customer Success Manager Requirements

Here is the list of some essential customer success manager duties:
Educational Background
While there’s no strict educational path for becoming a CSM, a bachelor’s degree in business, marketing, or a related field is often preferred. Advanced degrees can be advantageous but are not always necessary.
Relevant Work Experience
Experience in customer-facing roles such as sales, account management, or customer support is beneficial. This background helps CSMs understand customer needs and how to address them effectively.
Essential Skills and Competencies
A successful CSM possesses a blend of soft and hard skills. Key competencies include empathy, active listening, strategic thinking, and the ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously.
Technical Proficiency
Proficiency with customer success software, CRM systems, and other relevant tools is essential. This technical knowledge enables CSMs to efficiently manage customer interactions and data.
Customer-Centric Mindset
A strong focus on customer satisfaction and success is fundamental. CSMs must prioritize customer needs and work diligently to exceed their expectations.
Effective Communication Skills
Clear and effective communication is crucial for a CSM. They must be able to convey complex information in a straightforward manner, both verbally and in writing.
Problem-Solving Abilities
CSMs encounter a variety of challenges and must be adept at solving problems quickly and effectively. This skill is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and trust.
Experience Needed for a Customer Success Manager
Industry Experience
Familiarity with the industry in which a company operates can provide valuable insights into customer needs and expectations. Industry experience helps CSMs offer more relevant and effective support.
Familiarity with Customer Success Software
Experience with customer success platforms and tools is essential for efficient workflow & customer success management. Familiarity with these tools helps CSMs track customer interactions, monitor progress, and automate routine tasks.
Experience in Account Management
Account management experience is highly relevant, as it involves similar skills and responsibilities. This background helps CSMs manage customer relationships and expectations effectively.
Experience in Cross-Functional Collaboration
Working with various departments such as sales, marketing, and product development is a regular part of a CSM’s role. Experience in cross-functional collaboration ensures seamless coordination and better customer outcomes.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Being able to reference past successes and case studies can be a powerful tool for CSMs. These examples demonstrate their ability to deliver results and provide valuable insights for future strategies.
Continuous Learning and Development
The field of customer success is constantly evolving. A commitment to continuous learning and professional development helps CSMs stay updated with the latest trends, tools, and best practices.
Tools and Technologies for Customer Success Managers
Here are the tools and technologies for customer success managers:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
CRM systems are essential for managing customer interactions and data. They help CSMs track customer progress, monitor communication, and maintain comprehensive records.
Customer Success Platforms
Dedicated customer success platforms offer tools specifically designed for CSMs. These platforms provide features for onboarding, monitoring customer health, and managing renewals and upsells.
Communication Tools
Effective communication is facilitated by tools such as email, chat, and video conferencing. These tools enable CSMs to stay in constant contact with their customers.
Analytics and Reporting Tools
Data-driven decision-making is supported by robust analytics and reporting tools. These tools help CSMs analyze customer data, track performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Knowledge Base and Self-Service Tools
Providing customers with access to a knowledge base and self-service tools empowers them to find solutions independently. This reduces the workload on CSMs and enhances customer satisfaction.
Will AI Replace Customer Success Managers?
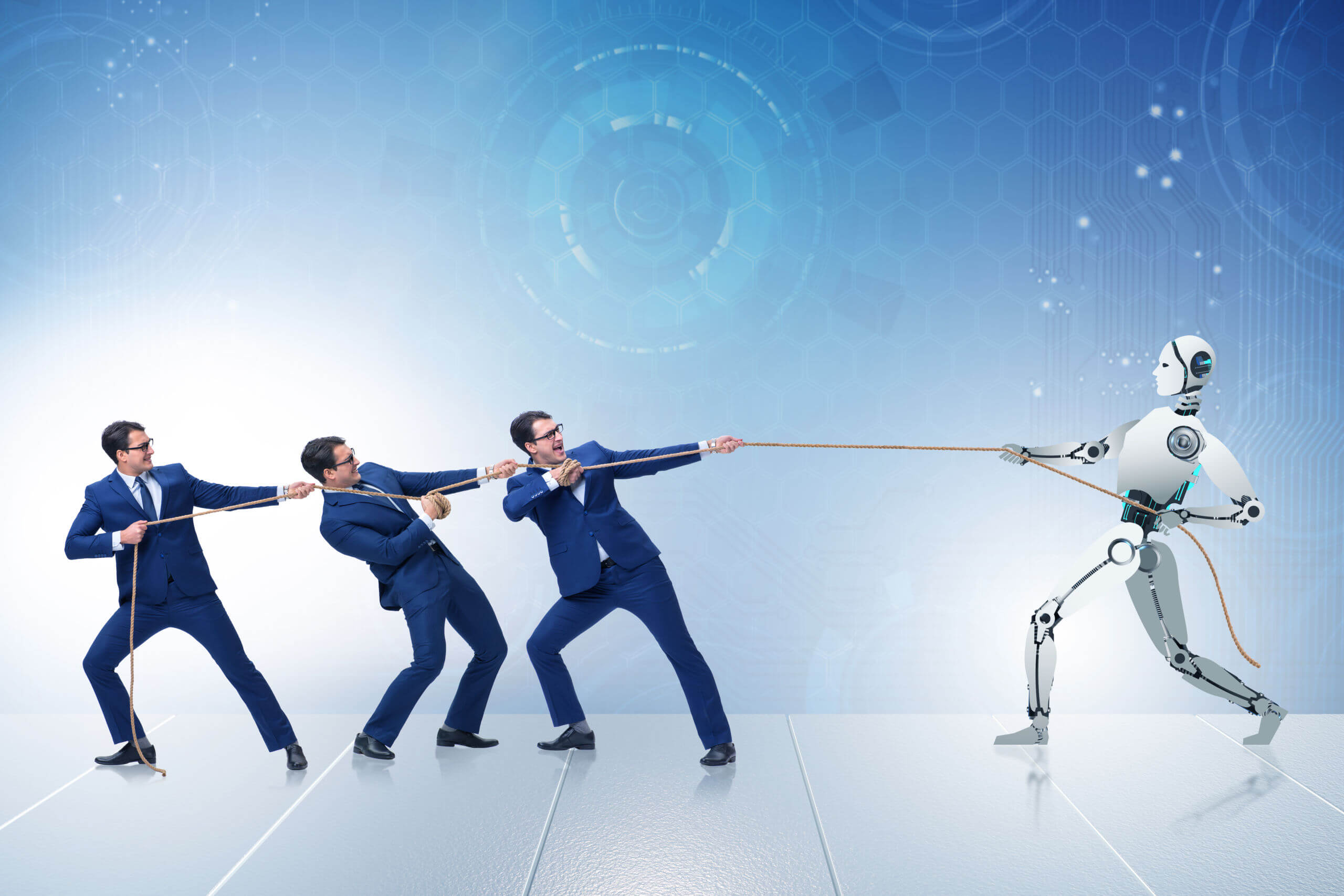

While AI technology is advancing rapidly, it's unlikely to fully replace Customer Success Managers (CSMs). AI can automate repetitive tasks, analyze large datasets, and provide insights that enhance decision-making.
For instance, AI shopping assistants can offer personalized product recommendations and instant support, improving customer experience. However, the role of a CSM involves building deep, personal relationships with customers, understanding their unique needs, and providing tailored support that requires human empathy and intuition.
Manifest AI, a leading AI platform, exemplifies how AI can assist rather than replace CSMs. It helps CSMs by streamlining workflows, identifying potential issues before they escalate, and offering data-driven insights.
This allows CSMs to focus on more strategic tasks that require human judgment and creativity. Therefore, AI serves as a powerful tool to augment the capabilities of CSMs, enabling them to deliver more effective and personalized customer success strategies.
FAQs
What do customer success managers do?
Customer Success Managers (CSMs) help customers use a company's product or service effectively to achieve their goals. They guide new customers through the onboarding process, provide training and support, monitor customer satisfaction, and address any issues that arise. CSMs also maintain regular communication with customers to ensure their needs are met and work to build strong, long-term relationships. Their goal is to ensure customers are happy and successful, which helps in retaining them and fostering loyalty.
How to become a customer success manager?
To become a Customer Success Manager, start with a bachelor's degree in business, marketing, or a related field. Gain experience in customer-facing roles such as sales or support, and develop strong communication and problem-solving skills. Familiarize yourself with customer success tools and best practices through continuous learning and professional development.
How much does a customer success manager make?
A Customer Success Manager typically earns between $60,000 and $90,000 per year, depending on their experience and location. Senior positions or those in major tech hubs can see salaries upwards of $100,000. Bonuses and commissions may also contribute to their total compensation.

.png)
