Inventory Reconciliation: The Secret to a Balanced Business

Inventory reconciliation is the process of comparing your physical inventory records to your accounting records. It is an important process for businesses of all sizes, as it helps to ensure that your inventory records are accurate and that you are not losing money due to theft, shrinkage, or other errors.
When your inventory records are accurate, you can make better decisions about your business. For example, you can know how much inventory you need to order to meet customer demand, and you can avoid overstocking or understocking. Accurate inventory records can also help you to track your costs and profits more effectively.
In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of inventory reconciliation and the steps involved in the process. We will also provide tips for making inventory reconciliation easier and more efficient.
What is inventory reconciliation in detail?
Inventory reconciliation is the process of comparing physical inventory counts to inventory records. This is done to ensure that the records are accurate and that all inventory is accounted for. Inventory reconciliation is important for businesses of all sizes, as it can help to prevent theft, shrinkage, and other errors.
Why is inventory reconciliation important?
Inventory reconciliation is important for several key reasons in the world of business and accounting:
- Financial Accuracy: Accurate inventory records are essential for producing reliable financial statements. Inventory is a significant asset for many businesses, and its valuation affects a company's balance sheet and income statement. Proper reconciliation ensures that a company's financial statements accurately reflect its assets and liabilities.
- Cost Control: By regularly reconciling inventory, businesses can identify discrepancies and address them promptly. This helps prevent overstocking or understocking situations, which can lead to increased carrying costs or lost sales opportunities. Effective inventory management can lead to cost savings and improved profitability.
- Operational Efficiency: Accurate inventory data is crucial for efficient day-to-day operations. It ensures that products are available when needed and prevents stockouts that can disrupt production or sales. It also helps minimize the holding of excess inventory, freeing up working capital.
- Reduction of Shrinkage and Losses: Inventory shrinkage, which includes factors like theft, damage, and spoilage, can significantly impact a company's profitability. Regular reconciliation can help detect and address shrinkage issues, reducing financial losses.
- Compliance: In certain industries and for regulatory purposes, accurate inventory records are a legal requirement. Ensuring compliance with industry standards and government regulations is crucial to avoid penalties and legal consequences.
- Decision-Making: A statistical inventory reconciliation provides valuable insights for decision-makers. Accurate inventory data helps businesses make informed decisions about production scheduling, procurement, pricing, and sales strategies.
- Budgeting and Planning: Reconciliation helps in budgeting and forecasting. Businesses can plan for future inventory needs more effectively when they have a clear understanding of their current inventory levels and valuation.
- Investor and Stakeholder Confidence: Reliable financial reporting, backed by accurate inventory data, enhances investor and stakeholder confidence. Transparent and accurate financial statements contribute to a positive reputation in the market.
- Risk Management: Effective inventory reconciliation is part of risk management. It helps identify and mitigate risks associated with inventory inaccuracies, ensuring that the company's assets are adequately protected.
- Internal Control: Inventory reconciliation is part of internal control procedures within an organization. It helps maintain the integrity of financial data and safeguards against fraud or misappropriation of assets.
What are the four types of reconciliation?
Reconciliation is a process of comparing two sets of records or accounts to ensure they match and are accurate. There are several types of reconciliation, but the four most common ones include:
- Bank Reconciliation: This type of reconciliation involves comparing your company's financial records (such as your accounting software or ledger including small business accounting software) with your bank statements. The goal is to ensure that all transactions, deposits, withdrawals, and fees recorded in your books match the information provided by your bank. Bank reconciliation helps identify discrepancies, such as outstanding checks or bank errors, and ensures that your financial records accurately reflect your actual cash position.
- Inventory Reconciliation: Inventory reconciliation, as mentioned earlier, involves comparing your recorded inventory levels with the actual physical inventory you have on hand. It helps ensure that your inventory records accurately represent the quantity and value of goods you have in stock. This type of reconciliation is essential for managing costs, preventing overstocking or understocking, and maintaining accurate financial statements.
- Account Reconciliation: Account reconciliation refers to the process of comparing and verifying transactions recorded in your financial accounts, such as accounts payable and accounts receivable, with corresponding records from your suppliers or customers. For accounts payable, you ensure that your records match the invoices received from suppliers, while for accounts receivable, you verify that your records align with payments received from customers. Account reconciliation helps maintain accurate records and supports effective cash flow management.
- Credit Card Reconciliation: Credit card reconciliation involves comparing your credit card statements with your internal records of credit card transactions. This process ensures that all credit card charges, payments, and fees are accurately recorded. It helps identify discrepancies, errors, or fraudulent transactions and ensures the accuracy of your financial records.
Inventory reconciliation best practices
Certainly! Here are the top 10 best practices for inventory reconciliation:
- Regular Reconciliation: Conduct reconciliation in inventory on a consistent schedule, such as monthly or quarterly.
- Well-Defined Procedures: Establish clear and documented procedures for the reconciliation process.
- Accurate Starting Point: Begin with accurate opening balances, ensuring they match the results of the previous reconciliation.
- Use Technology: Utilize inventory management software and barcode systems for accuracy and efficiency.
- Physical Counts: Regularly perform physical counts of inventory items.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of the reconciliation process, including personnel involved and discrepancies found.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigate and address the root causes of discrepancies.
- Adjust Inventory Records: Make necessary adjustments to bring inventory records in line with physical counts.
- Reconciliation Reports: Generate reports summarizing the results for management review.
- Continuous Improvement: Use insights gained from reconciliation to implement ongoing improvements in inventory management practices.
Inventory reconciliation: pros & cons
Inventory reconciliation is a crucial process for businesses, but like any process, it comes with its own set of advantages (pros) and potential challenges (cons). Here's a breakdown of the pros and cons of inventory reconciliation:
Pros of Inventory Reconciliation
- Accuracy: The primary advantage of inventory reconciliation is improved accuracy in your financial records. It ensures that the quantities and values of your inventory items in your books match the physical stock on hand.
- Cost Control: By identifying discrepancies and addressing issues promptly, you can control costs associated with inventory, reduce carrying costs, and prevent overstocking or understocking situations.
- Operational Efficiency: Accurate inventory data helps ensure that products are available when needed, preventing stockouts that can disrupt production or sales. It also optimizes inventory turnover and helps in efficient order fulfillment.
- Preventing Shrinkage: Regular reconciliation helps identify inventory shrinkage, including theft, damage, or spoilage, allowing you to take corrective action to reduce financial losses.
- Decision-Making: Reliable inventory data provides valuable insights for decision-makers, enabling informed decisions about production, procurement, pricing, and sales strategies.
- Budgeting and Planning: Accurate inventory records support effective budgeting and forecasting, helping businesses plan for future inventory needs.
- Compliance: In industries with regulatory requirements, reconciliation in inventory ensures compliance with standards and regulations, reducing the risk of penalties or legal consequences.
- Investor and Stakeholder Confidence: Transparent and accurate financial statements backed by inventory reconciliation enhance investor and stakeholder confidence.
Cons of Inventory Reconciliation
- Time-Consuming: Inventory reconciliation can be a time-consuming process, particularly for businesses with large inventories. It may require significant resources, including personnel and technology.
- Disruption: Conducting physical counts and reconciling inventory can disrupt normal business operations, particularly if it involves temporary closures or reduced productivity.
- Complexity: Inventory reconciliation can be complex, especially for businesses with multiple locations, various product categories, or global operations.
- Costs: While it can lead to cost savings in the long run, inventory reconciliation itself may incur expenses, such as labor costs, software costs, or the costs associated with implementing process improvements.
- Potential for Errors: Human errors can occur during the reconciliation process, particularly when manual counting and data entry are involved. These errors can lead to inaccuracies in records.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing inventory reconciliation processes and changes in inventory management practices may face resistance from employees accustomed to existing methods.
- Resource Intensive: Smaller businesses with limited resources may find it challenging to allocate personnel and technology for regular inventory reconciliation.
Inventory reconciliation template
Here is an inventory reconciliation example for your knowledge:
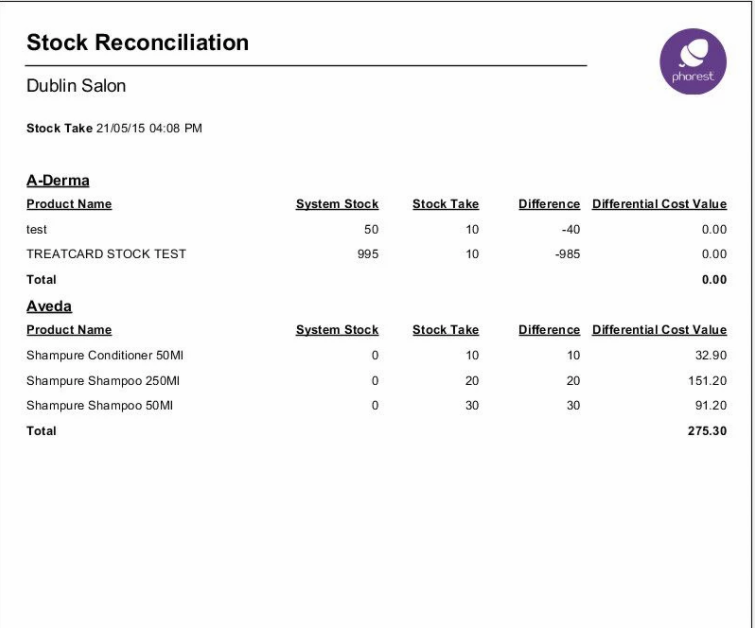
Conclusion
Inventory reconciliation is a critical process for any business that wants to stay afloat. By accurately tracking your inventory levels, you can avoid costly mistakes like overstocking or understocking, identify and prevent theft and shrinkage, and make better business decisions overall.
In today's competitive marketplace, it's more important than ever to have a balanced business. Inventory reconciliation is one of the secrets to achieving this balance. By taking the time to implement a regular inventory reconciliation process, you can ensure that your business is on the path to success.
FAQs
Here are the frequently asked questions related to inventory reconciliation:
What is a inventory reconciliation formula?
Closing Inventory = Opening Inventory + Purchases - Sales
This formula helps businesses determine the closing inventory value at the end of a specific accounting period. It takes into account the starting inventory, additional purchases, and subtracts the sales made during that period to arrive at the closing inventory value.

.png)
