MBR or GPT: Difference between an MBR Partition and a GPT Partition

When it comes to partitioning a hard drive, understanding the difference between MBR and GPT is crucial. These two partitioning schemes have distinct characteristics, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact your system's performance and compatibility. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of MBR and GPT, helping you make an informed decision for your storage needs.
What is MBR?
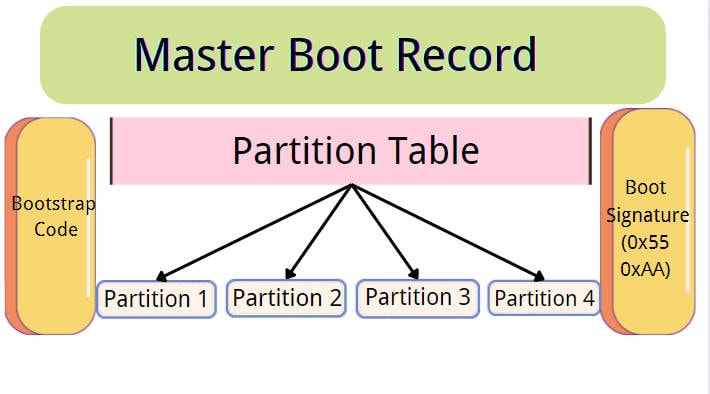
MBR, or Master Boot Record, is one of the oldest partitioning schemes used in personal computing. Developed in 1983, MBR has been the standard for many years and is still widely used today.
History of MBR
The MBR partitioning scheme was introduced with IBM PC DOS 2.0 and has since been a fundamental part of PC architecture. Its simplicity and wide compatibility made it a go-to choice for decades.
Structure of MBR
The MBR is located at the very beginning of a storage device, containing the boot loader and partition table. The boot loader is responsible for loading the operating system, while the partition table holds information about the partitions on the drive.
Advantages of MBR
- Compatibility: MBR is supported by almost all operating systems and BIOS firmware, making it a versatile choice.
- Simplicity: Its straightforward design makes it easy to use and understand.
Limitations of MBR
- Partition Size Limit: MBR supports drives up to 2 TB in size. Any larger capacity must be handled with another partitioning scheme.
- Limited Partitions: MBR can only manage up to four primary partitions. To create more, you need to set up an extended partition with logical partitions inside it.
- Data Integrity: The single point of failure at the MBR can lead to boot issues if it becomes corrupted.
What is GPT?

GPT, or GUID Partition Table, is a more modern partitioning scheme that overcomes many of the limitations of MBR. It is part of the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) standard, providing better performance and security.
History of GPT
GPT was introduced as part of the UEFI standard to address the growing need for a more robust and flexible partitioning scheme, capable of supporting larger drives and more partitions.
Structure of GPT
GPT stores multiple copies of the partition table across the disk, enhancing data integrity. It uses globally unique identifiers (GUIDs) for each partition, ensuring no conflicts and better organization.
Advantages of GPT
- Larger Drives: GPT supports drives larger than 2 TB, making it suitable for modern storage needs.
- More Partitions: GPT allows for an almost unlimited number of partitions, with the typical limit being 128 in Windows.
- Data Integrity: Redundant partition tables and CRC32 checksums improve the reliability and recoverability of data.
Limitations of GPT
- Compatibility Issues: Older systems with BIOS firmware may not support GPT, requiring UEFI firmware to utilize its full potential.
What is a Partition Scheme?
A partition scheme is a method of dividing a storage device into distinct regions, each capable of functioning as a separate disk. These regions, or partitions, help organize data, manage files, and install multiple operating systems.
Difference between MBR and GPT
Partition Size Limits
MBR can handle drives up to 2 TB, whereas GPT can manage drives of any size, limited only by the operating system's capabilities.
Number of Partitions
MBR supports up to four primary partitions, or three primary and one extended partition. GPT allows for a significantly higher number of partitions, generally up to 128 in Windows.
Compatibility
MBR is widely compatible with most older operating systems and BIOS firmware. GPT requires UEFI firmware, making it less compatible with older systems but ideal for newer ones.
Data Integrity and Recovery
GPT provides enhanced data integrity with multiple copies of the partition table and checksums. MBR has a single point of failure, making data recovery more challenging if corruption occurs.
Boot Process
MBR uses a traditional BIOS boot process, while GPT utilizes the more modern and flexible UEFI boot process, which supports faster boot times and more advanced features.
MBR or GPT for SSD
Choosing between MBR and GPT for SSDs depends on several factors:
- Disk Size: If your SSD is larger than 2 TB, GPT is necessary.
- System Compatibility: Ensure your system supports UEFI to use GPT.
- Future-Proofing: GPT is the better choice for modern systems, offering more partitions and better data integrity.
MBR or GPT for HDD
For HDDs, the choice between MBR and GPT hinges on similar considerations:
- Disk Size: HDDs larger than 2 TB require GPT.
- Number of Partitions: If you need more than four primary partitions, GPT is essential.
- System Type: Older systems with BIOS may necessitate MBR.
When to Use MBR?
Ideal Scenarios for MBR
MBR is best suited for older systems that do not support UEFI firmware or for drives smaller than 2 TB where compatibility with various operating systems is crucial.
System Compatibility Considerations
Systems running older operating systems like Windows XP or BIOS-only firmware should use MBR to ensure proper booting and partition management.
How to Check MBR or GPT
To check if a disk is MBR or GPT, follow these steps:
- Open Disk Management: Right-click on 'This PC' or 'My Computer' and select 'Manage.' Then, go to 'Disk Management.'
- Inspect Disk: Right-click the disk in question and select 'Properties.' Under the 'Volumes' tab, look for 'Partition Style.'
How to Convert MBR to GPT?
Here is the process to convert MBR to GPT:
Using Windows Disk Management
- Backup Data: Before converting, ensure all data is backed up to avoid any loss.
- Open Disk Management: Right-click on the Start button and select Disk Management.
- Delete Partitions: Right-click each partition on the MBR disk and choose "Delete Volume."
- Convert to GPT: Right-click the disk and select "Convert to GPT Disk."
Using Command Prompt
- Open Command Prompt: Run as Administrator.
- Use Diskpart: Type
diskpartand press Enter. - Select Disk: Type
list diskto find the disk number and thenselect disk X(replace X with the disk number). - Clean and Convert: Type
cleanfollowed byconvert gpt.
Data Backup Considerations
Always ensure your data is backed up before converting from MBR to GPT, as the conversion process will erase all existing partitions and data.
How to Initialize Disk GPT or MBR
When initializing a new disk, follow these steps to choose MBR or GPT:
- Open Disk Management: Right-click on 'This PC' or 'My Computer' and select 'Manage.' Then, go to 'Disk Management.'
- Initialize Disk: When prompted to initialize the disk, choose between MBR and GPT.
- Considerations: Choose GPT for larger disks and modern systems. Opt for MBR if compatibility with older BIOS systems is required.
Master Boot Record vs GUID Partition Table
Comparison at a Glance
- MBR: Suitable for older systems, limited to 4 primary partitions and 2 TB disks.
- GPT: Ideal for modern systems, supports more partitions and larger disks, with better data redundancy.
When to Use Each
- MBR: Use for legacy systems or smaller disks.
- GPT: Use for newer systems and larger disks.
FAQs
Can I convert MBR to GPT without losing data?
Yes, but it requires third-party tools. Always back up your data before attempting any conversion.
Is GPT faster than MBR?
GPT itself doesn't necessarily make your drive faster, but the UEFI boot process it supports can lead to faster startup times.
How do I know if my drive is MBR or GPT?
You can check this in Windows Disk Management by right-clicking on the disk and selecting "Properties." The "Volumes" tab will show the partition style.
Can older systems use GPT?
Older systems with BIOS firmware typically cannot boot from a GPT drive. They require UEFI firmware for full GPT support.
Why does Windows require GPT for some installations?
Windows requires GPT for installations on UEFI-based systems to take advantage of modern features and larger drive capacities.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between MBR and GPT is essential for managing your storage effectively. While MBR remains a reliable choice for older systems and smaller drives, GPT offers significant advantages for modern hardware, including support for larger drives, more partitions, and better data integrity. By choosing the right partitioning scheme, you can optimize your system's performance and ensure long-term compatibility.
FAQs
Should I Use MBR or GPT?
Deciding between MBR and GPT depends on your specific needs:
- Modern Systems: GPT is generally the best choice due to its advanced features and larger disk support.
- Older Systems: MBR may be necessary for compatibility with older BIOS firmware.
What is a GPT disk?
A GPT disk uses the GUID Partition Table scheme, supporting larger disks and more partitions, with better data integrity compared to MBR.

.png)
