What is GMV( Gross Merchandise Value): Meaning, Calculation & Benefits (2024)

Did you know that Amazon, the world's largest e-commerce company, posted a staggering $121 billion in Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) in just the second quarter of 2024? That's a massive amount of money pouring through their platform, and it's a strong indication of the thriving internet marketplace. But what is GMV, and why is it so significant?
Understanding GMV is critical for everyone participating in the e-commerce industry. It is the primary indicator used to calculate the total value of goods sold through a platform, providing vital insights into the performance and growth of a business.
Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just getting started in the internet business world, understanding GMV will help you make more informed decisions.
This blog post will go deep into the GMV, giving you with a clear description, a simple GMV formula for computation, and a thorough study of its benefits and drawbacks. By the end of this article, you'll have the knowledge and expertise to confidently navigate the e-commerce market and use GMV to your benefit.
What is GMV(Gross Merchandise Value)?
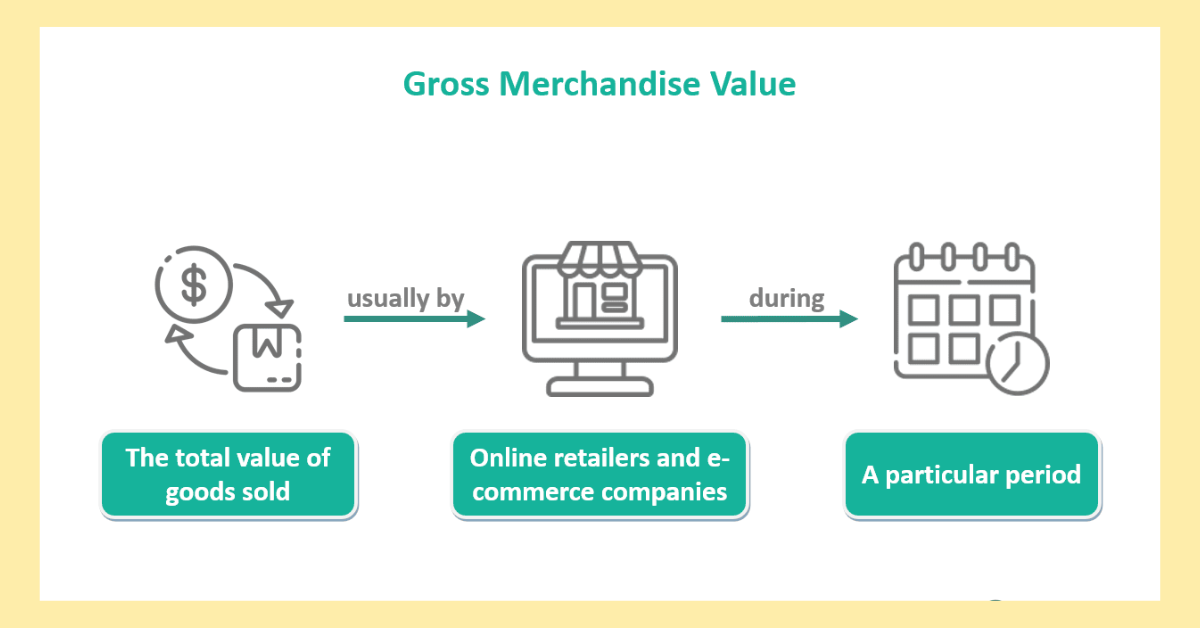
GMV (Gross merchandise value) is a measure that quantifies the total value of goods or services sold on a platform over a certain time period, excluding any discounts, returns, or refunds. It provides a comprehensive perspective of an e-commerce platform's or marketplace's entire sales volume. GMV is an important indicator for assessing an online business's overall success and scalability, although it excludes aspects such as operational costs and profit margins. In the e-commerce industry, it is frequently used to analyze the platform's scale and market presence.
What Is the Importance of GMV Retention?
GMV retention provides numerous advantages to e-commerce businesses:
Future Growth is Predicted: A high GMV retention rate indicates a steady and loyal client base, allowing for more accurate forecasting of future sales and revenue.
Identifies Growth Opportunities: Analysing GMV retention by product category, customer group, and region assists organisations in identifying areas where they can retain consumers more successfully and maximise their potential.
Improves Customer Acquisition: Retaining existing customers is frequently less expensive than obtaining new ones. Businesses may improve their customer experience and marketing efforts to attract and keep valuable consumers by understanding the elements that influence GMV retention.
Increases Profitability: Retaining consumers leads to increased profitability because they are more likely to spend more and make repeat purchases.
Improves Competitive Advantage: A strong GMV retention rate demonstrates a platform's ability to build a loyal customer base, setting it apart from competitors.
Benefits of GMV in Ecommerce
For various reasons, the Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) is an important indicator in ecommerce:
Scale Measurement: GMV provides a snapshot of an ecommerce platform's overall transactional volume, allowing businesses to measure the magnitude of their operations and follow progress over time.
Platform Performance: This metric measures how well an ecommerce platform performs in terms of facilitating transactions and attracting customers.
Investor Attraction: When analyzing the prospects of an ecommerce business, investors frequently utilize GMV as a significant statistic. A higher GMV might make a platform more appealing to investors by implying a larger market presence.
Benchmarking: GMV can be used by ecommerce organizations to compare their performance to industry benchmarks and competitors, assisting them in identifying areas for improvement or optimization.
Strategic Decision-Making: By giving insights into customer purchasing behavior, GMV data can help inform strategic decisions such as marketing budget allocation, inventory management, and expansion planning.
While GMV metrics are a useful indicator for analyzing transactional volume and business growth, it does not take into account costs, profitability, or a company's overall financial health. As a result, it should be used in conjunction with other financial measures to provide a complete picture of an ecommerce company.
How to calculate GMV?

In the e-commerce era, understanding Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) is critical since it provides a comprehensive evaluation of your sales volume and success. While the formula is straightforward (GMV = Number of Units Sold x Average Order Value), calculating it efficiently necessitates several procedures and considerations. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you master the procedure:
1. Establish the Time Period
Define the timeframe during which GMV should be calculated. This could be a single day, a week, a month, a quarter, or a year. Timeframe consistency is critical for tracking trends and comparing performance over time.
2. Collect Information
You'll need two important pieces of information:
Number of Units Sold: The total number of units (items) sold within the specified time period. This data is available through your sales reports or the dashboard of your e-commerce platform.
Average Order Value (AOV): AOV is computed by dividing total income by the number of orders placed during the specified period. For example, if you made $10,000 from 100 orders, your average order value (AOV) would be $100.
3. Apply the Formula
Once you have both data points, simply multiply them together using the following formula:
GMV = Number of Units Sold x Average Order Value (AOV)
4. Examine the Results
The resulting figure is your GMV for the specified time period. To acquire a thorough understanding of your company's financial health, combine this statistic with other indicators such as cost of goods sold, marketing expenses, and profit margin.
5. Compare and Monitor
Calculate GMV on a regular basis to track sales growth and discover trends. To understand your market position and discover opportunities for improvement, compare your GMV growth to industry benchmarks and competitor statistics.
What GMV Fails to Reveal? (Limitation)
While Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) provides useful information about a company's sales volume, it is critical to understand its limitations. GMV, like any single statistic, can give an incomplete picture and lead to incorrect conclusions if not correctly evaluated. Here's a closer look at what GMV fails to disclose:
1. Profitability: Gross merchandise value (GMV) focuses simply on the overall value of items sold, ignoring the expenditures incurred in creating those sales. It does not disclose the real profit or loss created, which is necessary for assessing a company's financial health.
2. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Because GMV does not include information regarding the expenses of obtaining new customers, it is difficult to judge the effectiveness of marketing and sales efforts.
3. Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): While GMV captures short-term sales, it does not provide long-term customer profitability. CLTV, which quantifies a customer's entire revenue generated throughout their engagement with the company, provides a more comprehensive view of customer value.
4. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Because GMV excludes the cost of procuring or manufacturing the products sold, determining the true profitability of each product category or transaction is challenging.
5. Return Rate: GMV excludes returned products, which can have a substantial influence on revenue and profitability. Businesses must consider return rates in addition to GMV to get a complete view of their sales performance.
6. Operational Efficiency: GMV does not provide any information on a company's operational efficiency. To evaluate total business performance, metrics such as fulfilment costs, inventory management, and marketing efficiency must be examined alongside GMV.
7. Customer Satisfaction: While gross merchandise value (GMV) represents sales volume, it does not directly evaluate customer satisfaction. To achieve long-term profitability, businesses must track consumer feedback and satisfaction levels.
8. Competitive Landscape:While GMV can be used to measure performance against competitors, it does not provide a complete view of the competitive landscape. To acquire a comprehensive picture of their competitive situation, businesses must analyse elements such as market share, pricing tactics, and product differentiation.
9. Market patterns: GMV measures past performance but does not forecast future patterns. To stay ahead of the curve and make educated strategic decisions, businesses must analyse market research, industry reports, and customer behaviour.
10. Sustainability: GMV does not account for a company's environmental or social impact. To guarantee ethical and sustainable growth, businesses must examine these elements in addition to GMV.
How to Increase Gross Merchandise Value
Increasing Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) for an ecommerce website involves strategic enhancements to both product offerings and customer experience. Here are some effective ways to achieve this:
Offer free shipping: Encourage larger purchases by offering free shipping thresholds. This can motivate customers to add more items to their carts to qualify for free shipping, thereby increasing the average order value.
Upsell and cross-sell products: Implement targeted upselling and cross-selling strategies on product pages and during the checkout process. Suggest related products or higher-end alternatives to customers to enhance their shopping experience and increase your GMV.
Add bundles: Create product bundles that offer items at a slightly lower price compared to buying them separately. Bundles not only provide value to customers but also help clear inventory faster.
Offer bulk discounts: Encourage customers to buy more with bulk discount offers. This can be particularly effective for products that are frequently used and have long shelf lives, encouraging shoppers to stock up and spend more.
Provide top-notch customer service: Exceptional customer service leads to higher customer satisfaction, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth. Ensure your customer service team is responsive, knowledgeable, and friendly, addressing customer issues and queries promptly.
GMV vs Revenue: Comparison
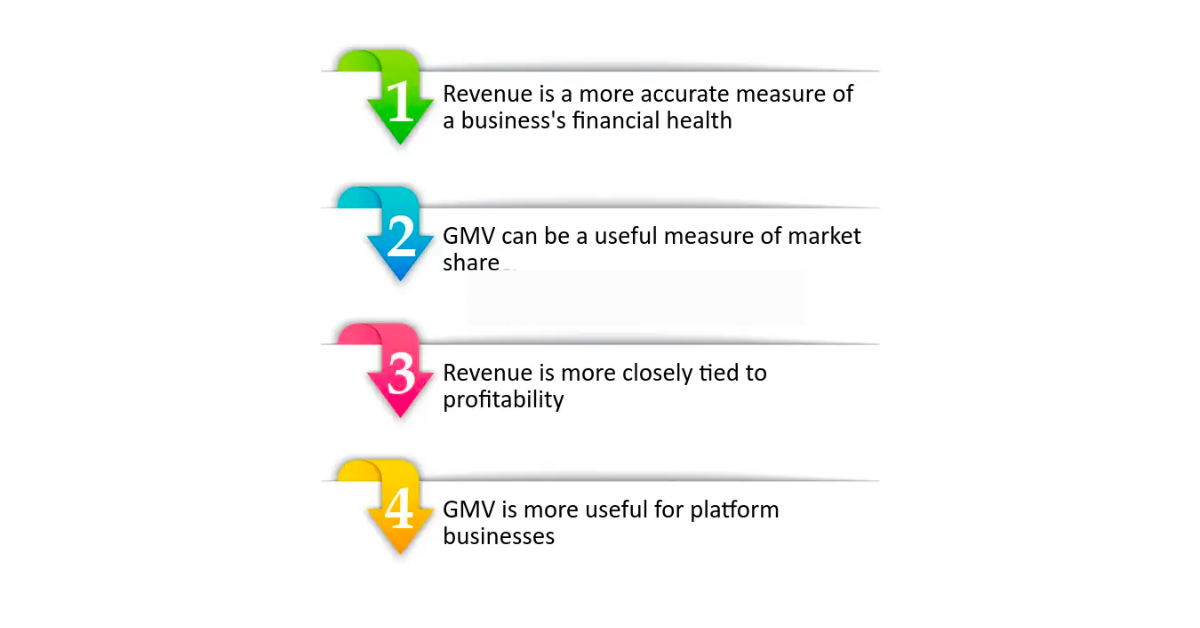
Understanding the difference between Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) and revenue is crucial for any e-commerce business. While both metrics provide valuable insights into your performance, they offer different perspectives and serve distinct purposes.
Here's a breakdown of their key differences:
Meaning
GMV: It represents the total dollar value of all goods sold through your platform during a specific period. This includes the full price paid by the customer, regardless of discounts, returns, or other adjustments.
Revenue: It represents the total income earned by your business from sales. It's calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS), returns, refunds, and other deductions from GMV.
Scope
GMV: Captures the total value of goods sold, even if they are returned or refunded later. This provides a comprehensive picture of the platform's sales volume and market reach.
Revenue: Focuses only on the income generated after deducting costs, returns, and discounts. This provides a clearer view of the business's financial health and profitability.
Calculation
GMV: Calculated by multiplying the number of units sold by the average order value.
Revenue: Calculated by subtracting costs (COGS, marketing, etc.) from the total sales revenue.
Purpose
GMV: Useful for understanding overall sales performance, tracking growth, and benchmarking against competitors.
Revenue: Crucial for analyzing profitability, assessing financial health, and making investment decisions.
Limitations
GMV: Doesn't provide direct information about profitability, as it doesn't consider costs or returns.
Revenue: Doesn't capture the total value of goods sold, making it difficult to assess the market reach and growth potential.
How can integrating Manifest AI into your Shopify store can improve GMV?
Integrating Manifest AI into your Shopify store can play a significant role in boosting your GMV:
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Manifest AI improves the overall shopping experience by providing real-time, AI-driven assistance. This level of customer service can increase customer satisfaction and repeat purchases, positively impacting GMV.
- Personalized Product Recommendations: By analyzing customer data and behavior, Manifest AI offers personalized product recommendations, encouraging customers to explore and purchase more items, thereby increasing the store's GMV.
- Efficient Query Handling: Quick and accurate responses to customer inquiries about products and services can lead to faster decision-making and purchases, contributing to higher GMV.
- 24/7 Availability: Its round-the-clock support ensures that customer queries are addressed at any time, potentially reducing cart abandonment and leading to higher sales.
- Multilingual Support: Catering to a global audience with multilingual capabilities, Manifest AI can attract and retain a broader customer base, which is crucial for increasing GMV.
Conclusion
To summarise, understanding Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) is critical for any company functioning in the e-commerce space. GMV delivers useful insights that educate strategic decision-making and promote business success as a complete assessment of sales volume and market reach. Businesses can unleash of opportunities for success in the competitive internet marketplace by understanding the simple math and comprehending its benefits.
Frequently asked question
What is GMV Marketing?
GMV marketing is a set of strategies designed specifically to increase Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) within the context of e-commerce. GMV represents the total value of goods sold through a platform over a specific period, making it a key metric for measuring success in this dynamic landscape.The primary goal of GMV marketing is to Attract and acquire new customers, Encourage existing customers to spend more, Increase overall sales and revenue, Drive sustainable growth for the business.
What is GMV in Ecommerce?
In e-commerce, Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) refers to the total value of goods sold through a platform over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It represents the total revenue generated before any deductions such as costs, returns, discounts, or taxes.

.png)
